ISRO Releases Images of Moon’s Impact Craters Snapped by Chandrayaan-2
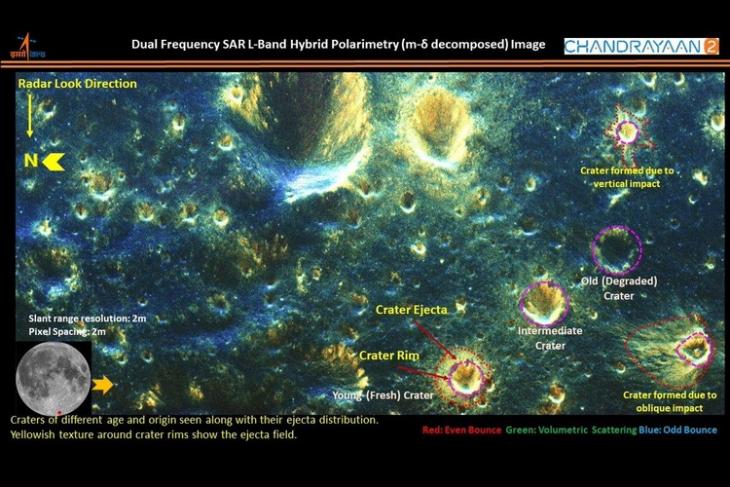

Indian space agency has released fresh set of pictures of touch on craters on moon surface taken by its Chandrayaan-two Orbiter. The Indian Space Research Arrangement (ISRO) on Tuesday, while releasing a flick on its Twitter handle, said the images were taken past the Dual Frequency-Synthetic Discontinuity Radar (DF-SAR) on its Chandrayaan-2 Orbiter.
Co-ordinate to ISRO, the Moon has been continuously bombarded by meteorites, asteroids and comets since its formation. This has resulted in the germination of innumerable impact craters that class the nigh distinct geographic features on its surface.
#ISRO#Chandrayaan2'due south DF-SAR is designed to produce greater details about the morphology and ejecta materials of impact craters on the lunar surface. Have a look of initial images and observations made by DF-SAR
For more than details please visit: https://t.co/1j7SBcXIpl pic.twitter.com/SEHukoYJMV
— ISRO (@isro) Oct 22, 2019
Impact craters are approximately circular depressions on the surface of the moon, ranging from modest, simple, bowl-shaped depressions to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. "In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain", ISRO said.
The report of the nature, size, distribution and limerick of impact craters and associated ejecta (cloth that gets thrown out on an impact) features reveal valuable information about the origin and evolution of craters. According to ISRO, weathering processes result in many of the crater physical features and ejecta material get covered by layers of regolith (sand, dust, loose rock and soil over a hard surface) making some of them undetectable using optical cameras.
The Indian space agency said, the SAR is a powerful remote sensing instrument for studying planetary surfaces and subsurface due to the ability of the radar signal to penetrate the surface. Information technology is also sensitive to the roughness, structure and composition of the surface fabric and the buried terrain.
Previous lunar-orbiting SAR systems such as the Southward-band hybrid-polarimetric SAR on ISRO's Chandrayaan-ane and the S & X-ring hybrid-polarimetric SAR on NASA'southward LRO, provided valuable data on the scattering characterisation of ejecta materials of lunar bear on craters, ISRO said.
However, L & S band SAR on Chandraayan-two is designed to produce greater details about the morphology and ejecta materials of bear on craters due to its ability of imaging with higher resolution (2 – 75m slant range) and full-polarimetric modes in standalone also as joint modes in South and L-band with wide range of incidence bending coverage (ix.5 degrees – 35 degrees).
In addition, the greater depth of penetration of L-band (3-5 meters) enables probing the cached terrain at greater depths. The 50&S band SAR payload helps in unambiguously identifying and quantitatively estimating the lunar polar water-ice in permanently adumbral regions, ISRO said. "Chandrayaan-2 Orbiter's DF- SAR has been operated in total-polarimetry mode- a gilt standard in SAR polarimetry, and is the first-ever by any planetary SAR instrument", ISRO said.
This image presents many interesting facts virtually the secondary craters of different ages and origins in the lunar south polar region, the space agency said. "The yellowish tone around crater rims in the prototype shows ejecta fields. The distribution of ejecta fields, whether uniformly distributed in all directions or oriented towards a particular side of a crater, indicates the nature of the impact", ISRO explained.
According to ISRO, the image shows craters of vertical touch and oblique affect on the tiptop-right and bottom-right, respectively. Similarly, the roughness of the ejecta materials associated with the impact craters indicates the degree of weathering a crater has undergone.
Three similar sized craters along a row on the lesser-right of the image show examples of immature crater, moderately weathered crater and an sometime degraded crater. Many of the ejecta fields seen in the paradigm are non visible in high-resolution optical image over the aforementioned region, indicating the ejecta fields are buried beneath regolith layers.
Source: https://beebom.com/iansisro-releases-images-of-moons-impact-craters-chandrayaan-2/
Posted by: saddlerbecrut.blogspot.com


0 Response to "ISRO Releases Images of Moon’s Impact Craters Snapped by Chandrayaan-2"
Post a Comment